-
-
-
-
What can we do about it?
-
-
-
-
-
Having completed investigations to understand the natural hazards in more detail, the next step is to understand and assess different types of adaptation or hazard management interventions.
The programme focus is now on this next step: “What can we do about it?”
Developing an adaptation approach in this complex setting will be challenging, . The most suitable adaptation approaches will need to be technically viable, affordable, and endorsed by the community and other programme partners.
We say “approaches” because it’s more likely to be combinations or sequences of hazards interventions to manage or adapt to the natural hazard impacts. These will probably include both shorter- and longer-term responses.
We will consider all types of response – engineering, land-use planning and civil defence. As an example, you can view one of our recent mitigation assessment reports here:
We want to be clear that no decisions have been made, and we continue to fully involve the community in our work.
In coming months, we will set out a decision-making process for input from the community, the regional and district councils, and other project partners such as Iwi and DOC. This process will likely need to be presented to Council for endorsement.
Below is a proposed high-level schedule for the key community engagement milestones throughout the programme.
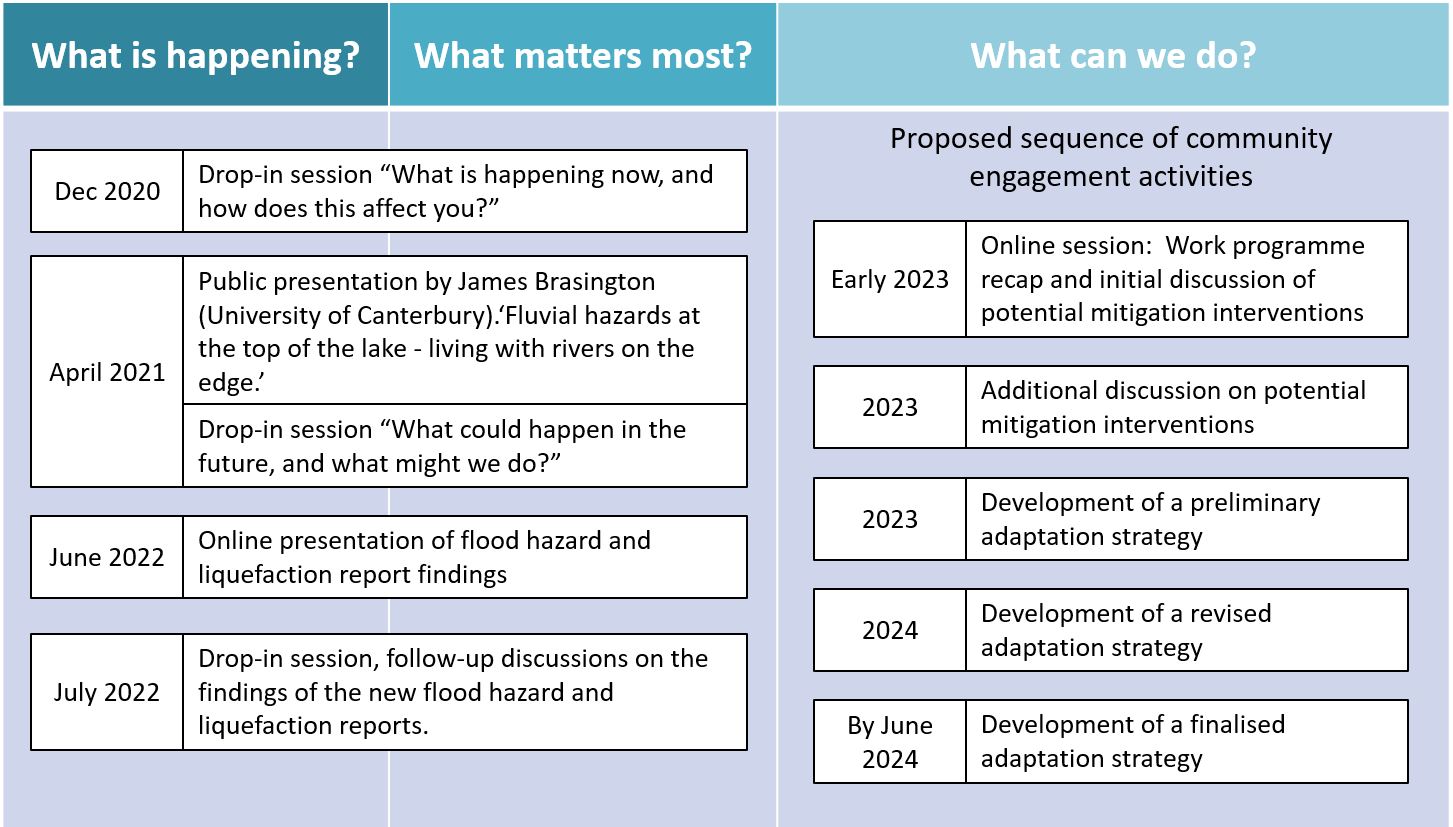
We are aiming to have a final agreed adaptation by the end of June 2024 (this a specified deliverable in the ORC Long-term Plan). The strategy is intended to be a living document, which will evolve in response to new information on hazard and risk, the needs of the community, and the work of the respective councils.
This strategy may include:
- a description of the strategy’s principles and strategic elements
- an action plan listing adaptation or hazards management interventions to be implemented, or which require further investigation
- greed trigger points for decision-making
- a river management strategy outlining the ORC’s approach to river management on the Dart-Rees floodplain
- response/recovery planning for major hazards events
- identification of knowledge gaps remaining in hazards and risk understanding, and a plan to investigate these
- a plan to review and reassess the strategy and its effectiveness (“How is it working?”).
Once the strategy document is complete, we will move into implementing the work programme.
Implementing some larger-scale adaptation or hazard management actions may be a long or costly process – we may need to integrate these actions with Council LTP processes, assess funding availability, develop business cases, and carry out further feasibility studies or cost-benefit analysis.
However, not all approaches will necessarily be costly or take a long time to implement. We may be able to implement some actions in the shorter term – these may include continuing to improve environmental monitoring and flood warning networks, Civil Defence planning, and continuing our river management approaches.
In 2022, ORC completed projects to assess flooding and liquefaction hazards in the head of Lake Wakatipu. You can read these reports here:
Following these technical assessments, ORC has received requests from community members to help better understand the risk levels of these natural hazard events, and how these risks compare with other locations around New Zealand.
Compared to previous hazards studies which have provided information of the characteristics of the natural hazard events, a risk assessment will consider in more detail the potential impacts and vulnerability to those events.
ORC will engage consultant experts to carry out this work, aiming to have it completed by mid-2023. Alongside a technical report, the consultant will also provide a plain-language summary of all findings, and will include comparisons of the natural hazard risks with other locations around New Zealand. For example, this might include comparison of the liquefaction risk at Glenorchy to that in Christchurch.