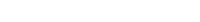We’re here to answer the questions you may have about the area, the adaptation programme and strategy, natural hazards, technical studies and more.
The answers below have been prepared by Otago Regional Council (ORC) staff using information from programme documents, reports and other sources. This page will be updated as new questions arise, so please get in touch if you have questions you’d like answered.
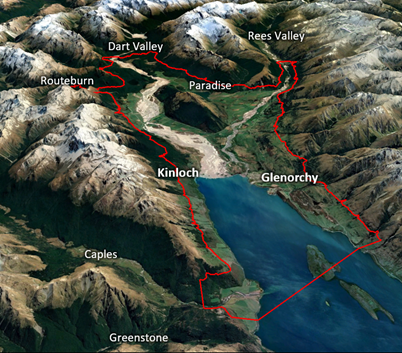
The Head of Lake Whakatipu (Whakatipu Waimāori) area is home to about 450 people (Stats NZ, 2018), living in the close-knit townships of Glenorchy and Kinloch as well as in rural areas such as Paradise, Rees and Greenstone Valleys, Campbelltown and Wyuna Preserve.
The area is located at the northern end (‘head’) of Lake Whakatipu and is the focus of our adaptation programmes. The area holds deep significance for mana whenua, with its ancestral mountains, rivers and lakes forming a network of taoka (treasure). These natural features, along with pounamu (greenstone) and tawhito (traditional travel routes), connected settlements, sustaining generations. The area’s ikoa wāhi (place names) weave together the stories and histories of Kāi Tahu, grounding their identity, heritage, spiritual connection to and authority in the land. These all make the area significant to the mana whenua.
A defining geographical feature of the Head of Lake Whakatipu area is the broad braided river systems and floodplains of the Dart and Rees rivers, which form a combined delta at the lake, lying between the Humboldt and Richardson mountains to the west and east, respectively. A braided river system is characterised by multiple interweaving channels that flow around gravel or sand islands.
The Head of the Lake has a dynamic landscape, with the Dart and Rees rivers having a nearly unlimited sediment supply, moving active channels and building up sediment, and growing the delta into Lake Whakatipu. High rainfall in the mountains feeds these rivers and often causes flooding that impacts local roads and important infrastructure as well as the community’s life and activities.
With a dynamic and seismically active environment, the Head of Lake Whakatipu area is exposed to a complex range of natural hazards, mainly flooding, landslides and earthquake-related hazards. These natural hazards can be relatively frequent and can be very disruptive. Climate and landscape changes could make some of these natural hazards worse.
The area is also exposed to seismic hazards including shaking, liquefaction and lateral spreading, partly due to its proximity to the Alpine Fault.
ORC initially undertook work to reduce flooding risks for Kinloch Road. However, it soon became clear that the wider area is exposed to multiple natural hazards—not just flooding, but also seismic-related risks. This led ORC to launch a broader, longer programme to better understand and proactively manage these risks both now and in the future for the communities in the area.
The Head of Lake Whakatipu natural hazards adaptation programme is a long-term initiative to develop a strategy for managing natural hazard risks and building resilience for communities in the Head of Lake Whakatipu area, including Glenorchy and Kinloch.
This programme takes a holistic approach to manage complex natural hazard challenges and uncertainties. It includes a wide range of work to support decision-making such as technical studies, community engagement, risk analysis, socio-economic impact assessment, adaptation options analysis and more.
The complex natural hazards in the Head of Lake Whakatipu area pose risks to the lives of people in the community and their social and economic activities, as well as critical infrastructure in the area. With a changing landscape and climate, these challenges are expected to intensify. While there are no simple solutions, taking adaptation actions now will lay the groundwork for stronger, more resilient communities in the Head of Lake Whakatipu—now and in the future.
ORC is using the Dynamic Adaptive Pathways Planning (DAPP) approach as a framework for the development of a natural hazards adaptation strategy for the Head of Lake Whakatipu area.
The ‘Adaptation Pathways’ approach has been developed by the Ministry for the Environment as a blueprint for community-led decision-making in areas affected by natural events and climate change. The approach will help plan and adapt to situations where the future is uncertain. It allows for flexible and adaptive decision-making, and for planning under conditions of uncertainty on the rate, timeframes and magnitude of future changes.
The Adaptation Pathways guidance is structured as a 10-step decision cycle, organised around five key questions:
- What is happening?
- What matters most?
- What can we do about it?
- How can we implement the strategy?
- How is it working?
The diagram below shows the DAPP approach:
The programme is currently at Step 8: Implementation.
Over the past few years, ORC, in partnership with Queenstown Lakes District Council and others, has undertaken a range of work to develop the natural hazards adaptation strategy. This includes technical studies and extensive community engagement.
The strategy has now been finalised, following several rounds of review by ORC teams, programme partners, and consultants. Community feedback gathered through both in-person sessions and online engagement also played a key role in shaping the final strategy document.
In May 2025, the strategy was endorsed by Otago Regional Council, and implementation begins from mid-2025.
‘Adaptation’ in its simplest form means making changes, adjustments to reduce the risks and impacts from natural hazards events like floods, helping communities stay safe and resilient.
In the context of the ORCs natural hazards adaptation programme, it is defined as a proactive response to anticipate and adjust to ongoing and future environmental changes. It is an ongoing process that involves identifying, assessing and managing risk while continually evaluating the effectiveness of actions and making necessary adjustments. This proactive, long-term approach enables planning and response in situations where the future is uncertain including variability in the rate, timeframe and magnitude of change (landscape, climate and socio-economic factors).
The Head of Lake Whakatipu Natural Hazards Adaptation Strategy (the Strategy) is a partnership between Otago Regional Council, Queenstown Lakes District Council, Civil Defence Emergency Management Otago, and the community.
It provides a common direction for our natural hazards management and adaptation planning and decisions at the Head of Lake Whakatipu (Whakatipu Waimāori). It also supports everyday decision-making by individuals and the community.
The Strategy has been developed over five years and is the result of a collective effort. A range of organisations, subject matter experts, and individuals have contributed.
Natural hazard resilience at the Head of Lake Whakatipu is reliant on a strong foundation of existing responses. Our Action Plan aims to build and improve upon this foundation.
As the landscape and climate change, we may need to consider big questions—do we do the same? Do things better? Do things differently? Our Future Toolbox contains possible responses that may help us adapt further as we face future changes.
Possible future responses are high-level concepts at this stage (not commitments). More information about detailed costs, benefits, and risks would be required to inform future decision-making.
Over time, we will review, adjust, and improve this first version of the Strategy. We will also track progress on our actions and check in with the community.
Mana whenua, key stakeholders, and the community are encouraged to continue their involvement in implementation and future versions.
The Strategy is a non-statutory plan. It does not carry decision-making power or create any legal obligations. Other statutory processes, such as long-term plans, also offer opportunities for public participation and alignment. This highlights the shared responsibility in managing natural hazards in the area, now and in the future.
Over many years, ORC has investigated flooding and other natural hazards at the head of the lake, including an investigation of natural hazards at Glenorchy in 2007 (findings reported in 2010).
We have also supported research projects, including a PhD project completed in 2012 that investigated the delta processes and characteristics.
Our Otago-wide studies of hazards – landslides, alluvial fans, and seismic hazards such as active faulting and liquefaction susceptibility – have all included the Head of Lake Whakatipu area.
All the information we have about natural hazards can be found on our Natural Hazards Database, which contains hazard maps, technical reports, and photographs from past events.
Also, all technical reports are located on our "Investigations and reports" page.
Neither the flooding hazard of the Dart-Rees floodplain nor the liquefaction hazard at Glenorchy township are new, but our studies have given us a more detailed understanding of these hazards.
Floods have been documented in the Dart-Rees floodplain and Glenorchy areas since early European settlement. Larger flooding events occurred in 1878, 1924, 1952, 1978, 1999, and more recently in March 2019 and February 2020.
Our first mapping of flood-prone areas of the Head of Lake Whakatipu area was based on observations from flooding events and interpretation of aerial imagery – this has been refined through subsequent studies.
In the early 2000s, several assessments identified the liquefaction hazard at Glenorchy. These earlier assessments were based largely on observations of the surface characteristics like the sedimentary deposits and interpretations of the groundwater table. The assessment by Tonkin+Taylor is the first to be based on detailed analysis, including deep geotechnical tests.
We commissioned two natural hazard investigations to refine our understanding of flooding hazards at the Dart-Rees floodplain and the liquefaction hazard at Glenorchy.
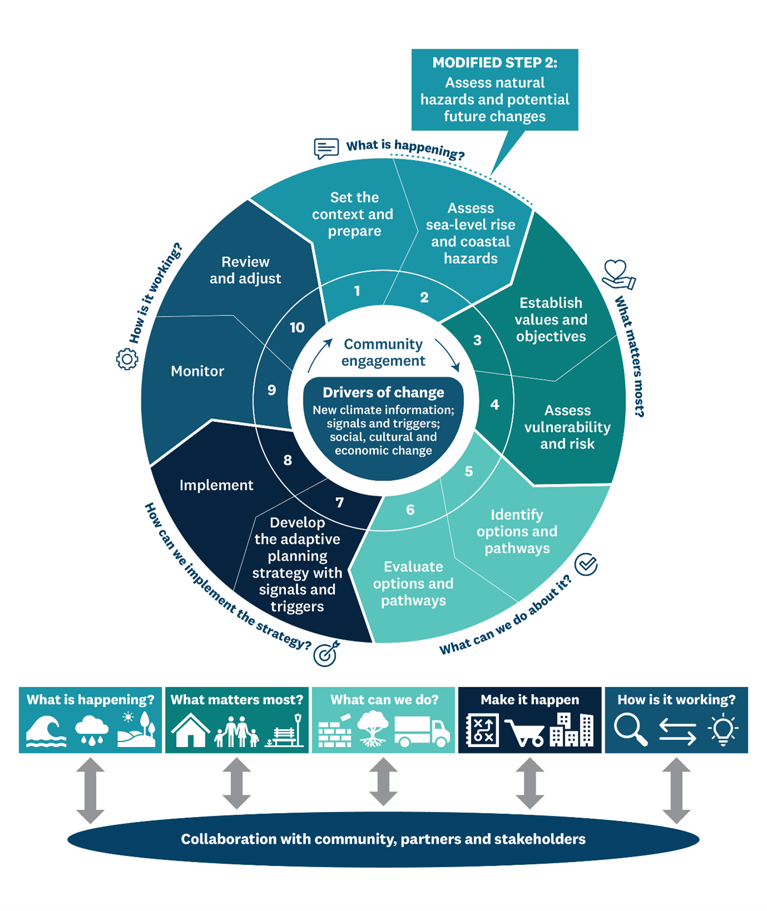
A geotechnical investigation by Tonkin + Taylor assessed how vulnerable the township is to liquefaction and lateral spreading caused by earthquake shaking, and the anticipated impacts of these hazards. The sediments underlying Glenorchy were investigated.
This report was based on geotechnical investigation of sediments underlying Glenorchy using data collected from boreholes and CPT (cone penetrometer tests). These were used to carry out an analysis of vulnerability to liquefaction and lateral spreading hazards.
At the same time, Land River Sea Consulting assessed the flood hazard to the Dart-Rees floodplain and Glenorchy from the Dart and Rees Rivers and high levels in Lake Whakatipu.
They modelled a range of very large flood event scenarios using a numerical model – for example, flooding events with a 1% chance of occurring in any one year, sometimes called the ‘100-year’ flood. Specific flooding scenarios modelled also included the impacts of climate change, a channel breakout (avulsion), and failure of a section of the Glenorchy floodbank.
The model results show the extent, depth, and speed of floodwater for each scenario, providing important information for assessing the flood hazards and possible impacts.
Both reports were peer-reviewed by independent experts.
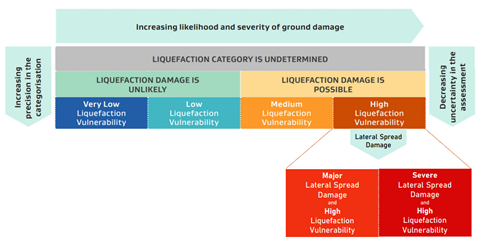
A new study of liquefaction hazards at Glenorchy has found that widespread ‘high to severe’ liquefaction damage is likely for all moderate to major earthquake scenarios, including an Alpine Fault rupture. Lateral spreading is also expected for some earthquake scenarios, which would cause severe ground deformation and damage in the western areas near the lakefront.
At Glenorchy township, geological investigations show that all of the sediments underlying the near-surface Buckler Burn gravels are highly susceptible to liquefaction.
A major earthquake and Alpine Fault rupture would likely cause ‘High to Severe’ liquefaction damages, comparable even to the 2010-2011 Christchurch earthquakes. In addition, lateral spreading would also cause severe ground deformation and damages in the western areas nearer the lakefront.
The map below shows the liquefaction hazard categorisation developed by T+T for liquefaction and lateral spreading hazards at Glenorchy. The hazard categorisation is based on New Zealand guidance from MBIE and MfE and is shown in more detail below.
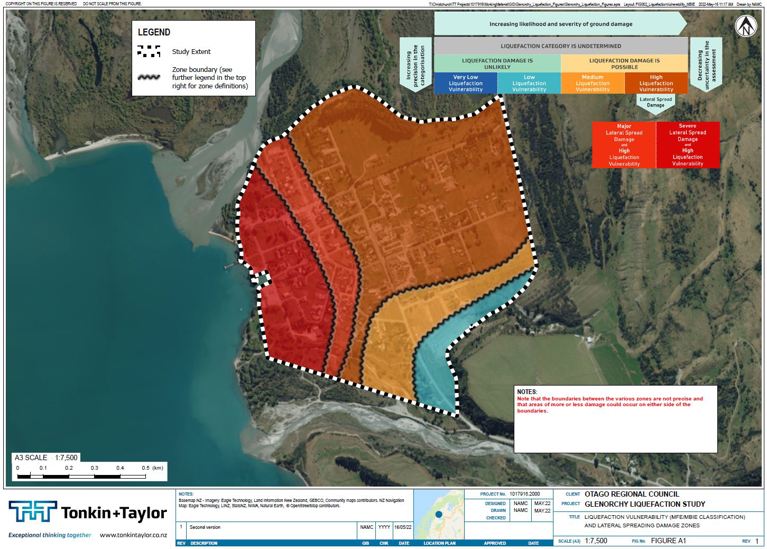
The Glenorchy area is exposed to a wide range of potential natural hazard risks such as flooding or alluvial fan activity, but other less frequent hazards such as earthquakes could also have a high impact. This area is only 40–50 km from the Alpine Fault and other active faults. Earthquakes could trigger other events such as liquefaction, landslides, and rockfall, or even a tsunami following a large landslide into the lake.
The flooding risks in the Glenorchy area are continually changing over time in response to natural processes and large-scale environmental changes. These include migration of the braided Dart and Rees rivers across their floodplains, growth of the Dart and Rees delta and landforms, and stream flooding activity across the many alluvial fans.
As the Dart and Rees deltas continue to grow into the lake, riverbed levels will also rise with ongoing sediment deposition, and the flood risk for the Glenorchy and Kinloch areas will increase. In addition, climate change is expected to bring more frequent and heavier rainfalls, increasing the flood risks for the rivers and lake. The potential impacts of these on people living in these areas are expected to increase, particularly for low-lying lakefront areas and floodplains.
The area encompasses the Head of Lake Whakatipu, including Glenorchy, Kinloch, and the surrounding rural Dart and Rees Valleys, Paradise, and Greenstone areas.
As well as Glenorchy, many of these other locations are exposed to several natural hazards such as flooding and erosion on the Dart and Rees floodplains, and flooding and debris flows from the tributary streams or hill slopes to the east and west.
An active fault – the West Whakatipu Fault – runs along the western side of Lake Whakatipu from Mount Nicholas towards the Routeburn Valley.
Modelling shows that in major flood events, such as an event with a 1% chance of occurring in any one year (a ‘100-year’ flood), there is widespread flooding in the northern parts of the Glenorchy township. Floodwaters may be deep (into the range of 1-2 metres) and fast flowing (into the range of 1-2 metres per second). Possible impacts of flooding have been assessed based on the modelled depth and velocity characteristics. This shows that in the areas of deepest and highest velocity floodwaters, it may be unsafe for both people and vehicles, and buildings may be vulnerable to structural damage.
The topography in the township is the main control of the flooding extents – as ground slopes up towards the south and southwest, those slightly higher areas are likely unaffected by flooding from the Rees River or Lake Wakatipu. However, note that the current flood hazard modelling project does not include other potential flooding sources, such as Bible Stream or the Buckler Burn. These flooding sources may affect areas outside the modelled flood extents of the current project.
The effects of climate change on river flows, or a breakout of the Rees River channel eastwards towards the Glenorchy lagoon, do not cause major increases in flooding hazard. In a major flood event, there would also be widespread flooding of the Dart and Rees floodplains.
Model results for the wider Dart-Rees floodplain area show large sections of Kinloch Road, as well as parts of the Glenorchy-Routeburn Road at the foot of Mount Alfred, would be inundated in a major flood event. These modelled events are similar, but even larger, than recent flooding events in this area, such as those in March 2019 and February 2020 (as pictured) (Image by Luke Hunter).

Liquefaction and lateral spreading can occur when strong ground shaking during an earthquake disturbs ground sediments, causing them to behave as a fluid.
The ground surface above liquefied soil can tilt and sink, affecting buildings, roads, and underground infrastructure, such as water supply and septic systems, to varying degrees.
Lateral spreading occurs when these liquefied soils move sideways, usually towards lower ground or water. When the soil underneath moves, cracks can also appear in the ground.

Landscape and climate changes are expected to cause increases in the severity and likelihood of natural hazard impacts to this area – particularly for rainfall-driven hazards such as flooding. This environment is very dynamic, with a long history of large-scale environmental changes. These include the migration of the braided Dart and Rees rivers across their floodplains, the growth of the Dart and Rees deltas (landforms created by sediment carried down the river to where it enters the lake), and common stream activity across the many alluvial fans.
As the Dart and Rees deltas continue to grow into the lake, the flood risk for the Glenorchy and Kinloch areas increases, and riverbed levels rise with ongoing sediment deposits. In addition, climate change is expected to bring more frequent and heavier rainfalls, increasing the flood hazard from the rivers and lake. The impact of these on people living in these areas is expected to worsen, particularly for low-lying lakefront areas and floodplains.

The risk analysis was based on natural hazards investigations previously completed for ORC. These include the flooding and liquefaction hazard assessments.
The scope of the Glenorchy and Kinloch Natural Hazards Risk Analysis study was to investigate risks from selected natural hazards by assessing a range of hazard scenarios.
The scope of the Assessment of Floodplain Intervention Options study was to investigate possible interventions to manage risks from flooding and erosion in the lower Rees River area by the Glenorchy township, the Dart River floodplain, and in the upper Rees River area by the Rees River bridge.
The findings from the risk analysis, floodplain intervention options, findings from previous studies, and community feedback will all be used to help develop the final Head of Lake Whakatipu Adaptation Strategy in 2025.
We have applied the risk assessment process and risk categories that are defined in the Otago Regional Policy Statement (2021). The Regional Policy Statement gives us a common approach to natural hazard risk assessment across the region and allows us to compare results between different places.
The labels used in the risk analysis to describe levels of risk are a bit different to how we would normally use these words in everyday life. These labels – ‘Acceptable, Tolerable, and Significant’ – will be used consistently in all natural hazards risk assessments ORC is completing across the region.
Acceptable risk is the level of risk that everyone affected is prepared to accept. Further actions to reduce this risk are usually not required unless they will cost little time, money, and effort.
Tolerable risk is risk that everyone affected can live with so long as the benefit gained from any intervention outweighs the cost.
Significant risk is a level of risk that is unacceptable or intolerable to the local community.
Every community will have what we call a different ‘tolerance’ for risk. The definition of ‘tolerance’ is based on different factors like individual and community resilience, how much disruption is considered ok, impacts on health and wellbeing, impacts on important sites or places, and the community’s experiences of past events.
The risk description labels ‘Acceptable, Tolerable, and Significant’ were developed with technical advice from risk specialists at GNS Science. You can find the full explanation of how we use a four-step process to determine the natural hazard risk in the Otago Regional Policy Statement (2021) on page 208.
Environmental monitoring of rainfall, river flows and lake levels provides a highly important dataset for understanding flooding events and for flood warning.
In the last two years, we have installed two new monitoring stations at Glenorchy and one in the Rees Valley.
These are:
- Glenorchy Lagoon water levels
- Rees River flows, measured near Invincible
- Lake Wakatipu levels, measured at the marina
These three new sites were all proposed by the community following the February 2020 flooding as actions to improve awareness of flood hazard.
Together with two older ORC monitoring sites in the Dart Valley, the current environmental monitoring network provides greatly improved monitoring coverage – this is summarised in the image below.
All of these sites are telemetered and their near real-time data can be viewed on ORC’s WaterInfo webpage.

ORC started the adaptation programme in mid-2019 and works in collaboration with key partners:
- Queenstown Lakes District Council
- Civil Defence Emergency Management Otago
- Mana whenua representatives (Aukaha)
- The community
- External consultants and experts.
The community has been a big part of shaping this adaptation strategy from the start. Over the past few years, many community members have come along to workshops, drop-in sessions, and meetings to share what matters to them—things like their values, hopes for the future, and ideas for looking after their place. This helped us understand what’s important and what the strategy needed to reflect. These insights were incorporated into the strategy’s vision, goals, and principles.
Community members also gave feedback on our technical studies and reports and helped explore different ways we could manage natural hazard risks in the area. Their local knowledge and ideas were key in identifying practical options and shaping possible pathways for the area’s future.
When we shared the draft strategy, the community provided thoughtful feedback that helped improve and finalise the document. This input made the strategy more effective, practical, and better connected to the people and places it’s designed to support.
The following are key responsibilities of ORC, QLDC, CDEM Otago, and the community:
- Community, individuals, private asset owners, and business owners are responsible for a range of activities, including emergency planning and arranging appropriate insurance for their businesses and properties.
- QLDC implements its activities through the Long-term Plan, Spatial Plan, and District Plan. This includes asset management, emergency and recovery planning, setting a long-term growth vision by identifying where homes, businesses, and infrastructure should be located, ensuring development avoids hazard-prone areas, supports community wellbeing, and applying land-use zoning, development rules, and building controls.
- ORC leads river management, monitoring, flood forecasting and warning, as well as emergency planning.
- CDEM Otago takes the lead and coordinates the 4Rs (reduction, readiness, response, recovery) and supports community response efforts.
-
Adaptation options/responses: The wide range of strategies and measures that are available and appropriate for addressing adaptation. They can take the form of structural, institutional, ecological or behavioural actions.
-
Adaptive capacity: The ability of systems, institutions, humans and other organisms to adjust to potential damage, to take advantage of opportunities or to respond to consequences.
-
Alluvial fan: An alluvial fan is a triangle-shaped deposit of gravel, sand and even smaller pieces of sediment, such as silt. This sediment is called alluvium.
-
Capacity building: The practice of supporting an individual, community, society or organisation to respond to change by enhancing their strengths and attributes and improving the resources available to them.
-
Climate change: Change in the state of the climate that can be identified (e.g., by using statistical tests) by changes or trends in the mean and/or the variability of its properties, and that persists for an extended period, typically decades to centuries. Includes natural internal climate processes and external climate forcings such as variations in solar cycles, volcanic eruptions and persistent anthropogenic changes in the composition of the atmosphere or in land use. The United Nations Framework Convention on Climate Change (UNFCCC) definition of climate change specifically links it to direct or indirect human causes, as: a ‘change of climate which is attributed directly or indirectly to human activity that alters the composition of the global atmosphere and which is in addition to natural climate variability observed over comparable time periods’. The UNFCCC thus makes a distinction between climate change attributable to human activities altering the atmospheric composition and climate variability attributable to natural causes.
-
Co-benefit: A positive effect that a policy or measure aimed at one objective has on another objective, thereby increasing the total benefit to society or the environment.
-
Disaster risk management: Processes for designing, implementing and evaluating strategies, policies and measures to improve understanding of current and future disaster risk, foster disaster risk reduction and transfer, and promote continuous improvement in disaster preparedness, prevention and protection, response and recovery practices. The aim is to increase human security, wellbeing, quality of life and sustainable development.
-
Dynamic adaptive pathways planning: A framework that supports climate adaptation decision-making by developing a series of actions over time (pathways). It is based on the idea of making decisions as conditions change, before severe damage occurs, and as existing policies and decisions prove no longer fit for purpose.
-
Hazard: The potential occurrence of a natural or human-induced physical event or trend that may cause loss of life, injury or other health impacts, as well as damage and loss to property, infrastructure, livelihoods, service provision, ecosystems and environmental resources.
-
Maladaptation: Actions that are unsustainable and may lead to increased risk of adverse climate-related outcomes, including increased greenhouse gas emissions, increased vulnerability to climate change and reduced welfare, now or in the future. Maladaptation is usually an unintended consequence. Some actions may be effective in some ways but maladaptive in others.
-
Nature-based solutions: Solutions that are inspired and supported by nature and are cost-effective, and at the same time provide environmental, social and economic benefits and help build resilience. Such solutions bring more, and more diverse, nature and natural features (e.g., vegetation and water features) and processes into cities, landscapes and seascapes, through locally adapted, resource-efficient and systemic interventions. For example, using vegetation (e.g., street trees or green roofs) or water elements (e.g., rivers or water treatment facilities) can help reduce heat in urban areas or support stormwater and flood management.
-
Pathways: NIWA (National Institute of Water and Atmospheric Research) describes pathways thinking as follows:
-
Pathways thinking is a planning approach that allows for the uncertainty and change by encouraging us to imagine many different futures. It does this by focusing on planning and that there will be many ways to find our way through the challenges of our future climate.
-
It takes into account what is important to individuals, whānau and communities. It helps us to consider the many different options in front of us; how long these might be effective for and when we might need to change tack.
-
Pathways thinking supports decision-making and investments in stages. It encourages people to identify triggers (for example a flood), and to make decisions in advance about what to do if that trigger occurs.
-
Using pathways thinking allows us to develop strategies for expected climate impacts, while not compromising or shutting off other options. This flexible approach recognises that conditions can change and means we avoid being locked in to any one course. Pathways thinking is an approach that is in the Ministry for the Environment's coastal hazards guidance and is being used by councils and others around Aotearoa as they plan how to adapt to a changing climate.
-
-
Resilience: Resilience has a broad range of definitions. In our context, it is the capacity and ability to withstand and/or recover quickly from difficult conditions. It also includes planning for unexpected events and supporting the wellbeing of our communities in adverse times.
-
Risk management: The process of making plans, actions, strategies or policies to reduce the likelihood and/or scale of potential adverse consequences, based on assessed or perceived risks.
-
Tolerable risk: Risk that society is willing to live with so as to secure certain benefits. Kept under review and may be further reduced as and when possible.
-
Uncertainty: A state of incomplete knowledge that can result from a lack of information or from disagreement about what is known or even knowable. It may occur for many reasons. For example, the data may be imprecise, definitions of concepts or terminology may be ambiguous, understanding of critical processes may be incomplete, or projections of human behaviour may be in doubt.
-
Vulnerability: The conditions determined by physical, social, economic and environmental factors or processes which increase the susceptibility of an individual, a community, assets or systems to the impacts of hazards.
ORC and its partners will begin implementing the strategy (mid-2025).
ORC will also prepare supporting materials to raise awareness and understanding of the strategy and assist the community and partners in implementing their activities.
Feel free to contact the ORC Natural Hazards Manager, Jean-Luc Payan, on 0800 474 082 or email us for more information at headofthelake@orc.govt.nz. This email will go to our Natural Hazards team, and we will provide responses to any emailed questions and facilitate answers from our consultants if needed.
You can also subscribe to our newsletter, which details news and progress as well as activities and upcoming community sessions.