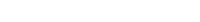-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
Ragwort
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-

Ragwort
| Common name: | Ragwort |
| Scientific name: | Senecio jacobaea |
| Management programme: | Sustained control |
Ragwort is toxic to grazing cattle, deer and horses as it causes liver cirrhosis (a late stage of scarring of the liver), photosensitisation (inflammation of the skin), jaundice (where the skin and whites of the eyes turn yellow) and wasting. Poisoned animals may take some months to die. Most animals avoid grazing ragwort. Sheep will eat it without any obvious effects, unless they are repeatedly exposed to it in large quantities or not used to feeding on it. It can dominate pasture, almost completely pushing out other pasture species in the worst cases, and significantly reduces the amount of grazing available to stock. Ragwort forms dense stands and is also invasive in riverbeds, disturbed forest and shrubland, coastal areas, bare land and other short-stature vegetation types. It usually disappears when a canopy (upper layer of forest) forms, which decreases light levels reaching the ground layer.
- Size: Ragwort commonly grows to 45–60 centimetres tall, but can grow to almost 2 metres high.
- Flowers: Produces bright yellow flowers in clusters from November to April.
- Distinctive feature: An erect herb with a one- or two-year life cycle.
The rule for ragwort only applies if you are on rural-zoned land. All occupiers of rural-zoned land must eliminate ragwort on their land within 50m of their boundary where the neighbouring property of that boundary is also controlling ragwort within 50m of the boundary.
This is a good neighbour rule, which means there are no unreasonable costs to land occupiers who are managing ragwort when their neighbours might not be. Non-compliance action on this rule will on happen if a complaint is made to ORC by the affected neighbour.
Spray
- You can spray rosette plants in the winter or spring before the stem has formed. Most ragwort will produce seeds in autumn so spraying in winter will kill most new seeds.
- Cover the entire plant, cut any seed heads and dispose of them by burning or deep burial.
Granules
- At any time of the year you can apply granules to the crushed centre of each plant. Make sure you also cut any seed heads and dispose of them by burning or deep burial.
Grubbing
- Grubbing works best with rosettes and early flowering plants; remove at least 5cm of the root to stop re-growth.
Caution: When using any herbicide or pesticide PLEASE READ THE LABEL THOROUGHLY to ensure that all instructions and safety requirements are followed.
www.orc.govt.nz/ragwort