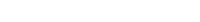-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
Chilean flame creeper
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-

Chilean flame creeper
| Common name: | Chilean flame creeper |
| Scientific name: | Tropaeolum speciosum |
| Management programme: | Site-led |
Chilean flame creeper is an invasive pest plant that can climb to canopy height (the upper layer of forests) and reduce light levels, smothering native bush and stopping native species from establishing.
Birds and pest animals eat the seeds, meaning Chilean flame creeper is easily spread. It survives in warm-to-cold temperatures, salt, wind, many soil types, and damp to dry conditions.
- Size: Chilean flame creeper is a climbing plant that can grow several metres tall.
- Leaves: Light green with five leaflets. Thin stems have curling tendrils (spiral threadlike leaves) and watery sap.
- Flowers: Single tubular scarlet flowers with five irregular petals: the bottom three having a very slim claw. After flowering, it has a thin, fleshy, deep-blue seed capsule made up of three round parts.
- Root system: It has a thick, well-developed root system.
- Habitat: Includes disturbed forests and shrublands.
Chilean flame creeper flowers appear from mid-spring to mid-autumn (November-April), making the plant easier to identify.
To prevent or improve on damage to indigenous ecosystems, Chilean flame creeper is in the site-led programme of the Otago Regional Pest Management Plan (2019-2029). The Dunedin site-led areas include West Harbour — Mt Cargill, Quarantine and Goat islands — and Otago Peninsula. There are no specific rules associated with site-led pest plants in the plan.
Chilean flame creeper is declared an unwanted organism in the National Pest Plant Accord. This means it cannot be sold or be in a place where plants are being sold. It cannot be propagated, bred, multiplied, communicated, released, caused to be released, or otherwise spread.
ORC will take a lead role in supporting the goals of community groups and agencies in site-led areas in relation to Chilean flame creeper. This may be through advice, education, funding, service delivery or requiring other landowners undertake to control when needed.
Physical control:
- Note that hand-pulling vegetation will have limited success as Chilean flame creeper is very hard to kill and rootstock and stems will resprout.
Chemical control:
- Cut the stump near the ground and paste it with a suitable herbicide gel, like Tordon BK, containing either metsulfuron, triclopyr or glyphosate.
- Spray foliage using a glyphosate-based product with penetrant and follow up every 6six months.
Note: while you can try the chemical control above, there is no fully effective herbicide treatment for Chilean flame creeper.
Caution: When using any herbicide or pesticide PLEASE READ THE LABEL THOROUGHLY to ensure that all instructions and safety requirements are followed.
Disclaimer: Mention of product trade names does not endorse these products nor imply criticism of similar products not mentioned. The Otago Regional Council does not give any warranty that the information is accurate or complete or that it is suitable for all circumstances.
Site-led
Site-led programmes have rules for specific pests that only apply in that area. Site-led areas have special biodiversity and other values to protect.
National Pest Plant Accord (NPPA)
Any plant listed on the NPPA is an unwanted organism under the Biosecurity Act 1993. This means they cannot be distributed or sold in New Zealand.

November 2019
Otago Regional Council
ISBN 978-0-908324-57-6
PDF | 5 MB
The Otago Regional Pest Management Plan focuses on dealing with harmful pests that impact our environment, economy, and communities. It identifies species like rabbits, wallabies, gorse, and wilding conifers that cause problems on our land. Guided by the Biosecurity Act 1993, the plan works with stakeholders to set rules and controls for managing pests. Through consultation, it aims to protect our region's unique ecosystems and species from the damage caused by these invasive organisms.

August 2025
PDF | 621 KB
Chilean flame creeper is an invasive pest plant that can climb to canopy height (the upper layer of forests) and reduce light levels, smothering native bush and stopping native species from establishing.
www.orc.govt.nz/chileanflamecreeper